
Body In Balance Thermography
About
Susan Barrett is a Certified Clinical Thermographic Technician. Susan provides a comprehensive thermal imaging service specializing in breast and full body imaging. Susan is also certified Massage and Lymphedema/Lymphatic Therapist specializing in women’s health such as cystic/lumpy painful breast, post mastectomy care, pelvic floor issues, pre/post menopausal symptoms, dysmenorrhea, amenorrhea, fertility, scar tissue, incontinence, fibroids, digestive health issues and more.
All images will be interpreted by Dr William Amalu, DC. Board Certified Clinical Thermologist and Diplomate in Clinical Thermography. Over 25 years of thermal imaging experience to patient care and provides thermogram interpreting services for many imaging centers worldwide. For more information go to www.breastthermography.com.
Spectron IR Medical Infrared Imaging System FDA 510(K) is certified and safe. Spectron IR is the exclusive manufacturer of the TyTron C-500 IR Clinical Infrared Imaging System is intended for adjunctive diagnostic screening for the detection of breast cancer and other uses such as: peripheral vascular disease, thyroid gland abnormalities, and various other neoplastic, metabolic and inflammatory conditions. Use of the TyTron C-500 is not intended to be a sole diagnostic procedure for these diseases and conditions.
What is Medical Infrared Imaging?
Medical infrared imaging is a painless imaging procedure that uses no radiation, injections or other invasive methods. It is a unique test that uses sophisticated medical infrared cameras and computer systems to image your body's surface temperature patterns. These patterns of heat are altered when biochemical messages from within the body changes the amount of heat given off at the surface of the skin. The test is painless, economical, FDA approved as an adjunctive imaging procedure and requires only an hour of your time.
What does it have to offer?
The technology may provide both early warning system and a method of analysis that may get to the cause of the problem that is not responding to treatment. Unlike other forms of imaging that detect structural changes such as tumor or a broken bone, infrared imaging looks at the body's subtle chemical and nervous system signals. These biochemical signals may aid in finding the cause of a current problem or one in advance of changes that can be seen on other tests. If the signals are an early warning, your doctor may be able to outline a method for preventing future problems before they cause irreversible damage.
What is the procedure like?
After completing a healty history from, you will be taken to a special temperature controlled imaging room. You will be asked to wear a gown and wait for a brief period while your body acclimates to the temperature of the room. The gown will be removed to expose the skin as multiple images are taken of the surface of the body. The whole procedure takes about one hour. You will be mailed a written report with copies sent to your health care provider at your request.
Who Benefits from Infrared Imaging?
Everyone! Especially health concious individuals who are looking for an important tool to add to their regular preventive health care. Infrared imaging may also give your doctor the information he or she needs to get to the cause of a current problem. By notifying you of a current problem that is going undetected, or possibly providing an early warning. Infrared imaging may be able to help you with health problems that rob you from enjoying life.
About Breast Cancer
Simply stated, cancer is a parasite. It is a mass of genetically malfunctioning cells with excessive incoordinate growth. Its growth is completely independent from all normal regulatory functions of the host and maintains law and order in its own terms.
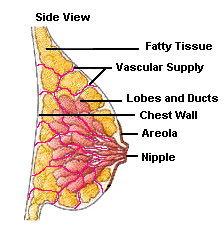
Why the Breast? To keep things simple, breast cancers emerge due to a combination of genetics, carcinogens, immune responses, hormones, and tissue composition. The breasts are composed of lobes, lobules, ducts, glands, and a high concentration of blood vessels and fat cells. Many of these tissues in the breast have receptors for the hormone estrogen, which makes them a target for the hormone’s influence. Some of this is good and some bad. Of particular interest are the fat cells. Fat cells both produce and breakdown estrogen. The chemical breakdown reaction (aromatization) of estrogen produces carcinogenic (cancer causing) byproducts. As a result, the carcinogens effect the DNA of nearby cells which can cause them to mutate into cancers. Research has shown that some women’s breasts are more susceptible than others to the effects of estrogen and its byproducts.
How Does the Cancer Grow? Once a normal cell begins to mutate (pre-cancerous tissue), its DNA is altered to allow for the onset of uncoordinated growth. To sustain the rapid growth of these pre-cancerous (and cancerous) cells, a constant supply of nutrients are needed. In order to maintain this supply, the cells release chemicals into the surrounding area which keep existing blood vessels open, awaken dormant ones, and create new ones (neoangiogenesis). The rich vascular beds in the breast provide the conditions necessary for the growing tumor’s needs.
How Can We Detect this Growth at its Earliest Stages? Current research suggests that a multimodal (multiple test) approach will detect more cancers at an early stage. Digital Infrared Imaging (DII or Breast Thermography) has the ability to detect the thermal signs of blood vessel changes that may suggest the development of a pre-cancerous as well as cancerous condition. Consequently, DII may be the first signal that such a possibility is developing.
Early Detection
Methods
Early Breast Cancer Detection Methods:
The following outlines the differences between mammography, medical infrared imaging (thermography), and ultrasound. Medical infrared imaging detects surface heat as a byproduct of biochemical reactions. As such, the test adds valuable physiologic information that cannot be obtained from any other imaging procedure. Thermography is designed to be used as an adjunct (an additional test) to a woman’s regular breast health care.
Mammography- (20% of cancers not detected), in women over age 50. Sensitivity decreases in women under age 50. Uses X-rays to produce an image that is a shadow of dense structures. This uses radiation that my cause cancer.
Ultrasound– (17% of cancers not detected), in all age groups. High frequency sound waves are bounced off the breast tissue and collected as an echo to produce an image.
Medical Infrared Imaging (Thermography)- (10% of cancers not detected), in all age groups. This is the best of the 3 methods because it is the most accurate and no use of radiation.
Note: A biopsy is the only test that can determine if a suspected tissue area is cancerous.

